Ecommerce Platform
In this chapter we will look at what designing a Ecommerce Platform like Amazon or Shopify looks like, but first let list out the functional requirements:
- HomePage: The homepage of an ecommerce platform can play a crucial role in the user experience, as it is often the first thing that customers see when they visit the site. A well-designed homepage can help customers find what they are looking for quickly and easily, and can also help drive sales and engagement. A recommendation system can be a key component of the homepage, as it provides personalized recommendations to each user based on their previous browsing and purchase history. This can help customers discover new products that they may be interested in, and can also help drive sales by suggesting products that the user is more likely to purchase.
- Search: The search feature is an essential component of any ecommerce platform. It should allow customers to easily search for products by keywords, product name, or category. The search algorithm should return relevant results, taking into account factors such as product popularity, relevance, and customer reviews. Additionally, the search feature should allow customers to refine their search results using filters such as price range, brand, color, size, and more.
- Cart/Wishlist: The cart or wishlist is where customers can store the items they want to purchase. The cart should be accessible from any page on the site, and customers should be able to add, remove, or modify items in their cart at any time. The wishlist should work similarly to the cart, but allow customers to save items they are interested in purchasing at a later time.
- Checkout: The checkout process is the final step in the ecommerce platform, and it should be seamless and secure. Customers should be able to review the items in their cart, select a shipping method, enter billing and shipping information, and choose a payment method. The platform should also provide a clear summary of the total cost, including taxes and shipping, and allow customers to apply promo codes or discounts.
- View Orders: The view orders feature should allow customers to view the details of their past orders, including the date of the order, the items purchased, the total cost, and the shipping and billing information. Customers should also be able to track the status of their orders, and see any shipping updates. This feature is important for customers to manage their past purchases and keep track of their spending on the platform.
Now for the non-functional requirements we will have the following:
- Low Latency: Low latency refers to the quick response time of an ecommerce platform, meaning that the platform should respond quickly to user requests. A low latency is important in ecommerce as it contributes to a smooth user experience and helps keep customers engaged. A platform with low latency will reduce the amount of time it takes to load pages, search for products, and complete transactions. A slow-responding platform can lead to frustration and a high bounce rate, as customers may abandon their shopping cart or navigate away from the site.
- High Availability: High availability means that the ecommerce platform should be available for use at all times, with minimal downtime. This is a critical requirement for an ecommerce platform as it ensures that customers can access the platform and make purchases whenever they need to. Downtime can result in lost sales, negative customer experiences, and a decrease in customer trust. A platform with high availability has multiple redundant systems in place to prevent downtime, such as load balancing and failover mechanisms, to ensure that the platform is always available and accessible to customers.
- High Consistency: High consistency in an ecommerce platform means that the results of a particular operation should be the same, regardless of the number of users or the time of day. For example, if a customer searches for a specific product, they should receive the same results each time they perform the search. High consistency is important in ecommerce because it builds customer trust in the platform, ensuring that customers can depend on the platform to provide accurate and reliable results. A platform with high consistency is less likely to experience errors or unexpected behavior, which can lead to frustrated customers and lost sales.
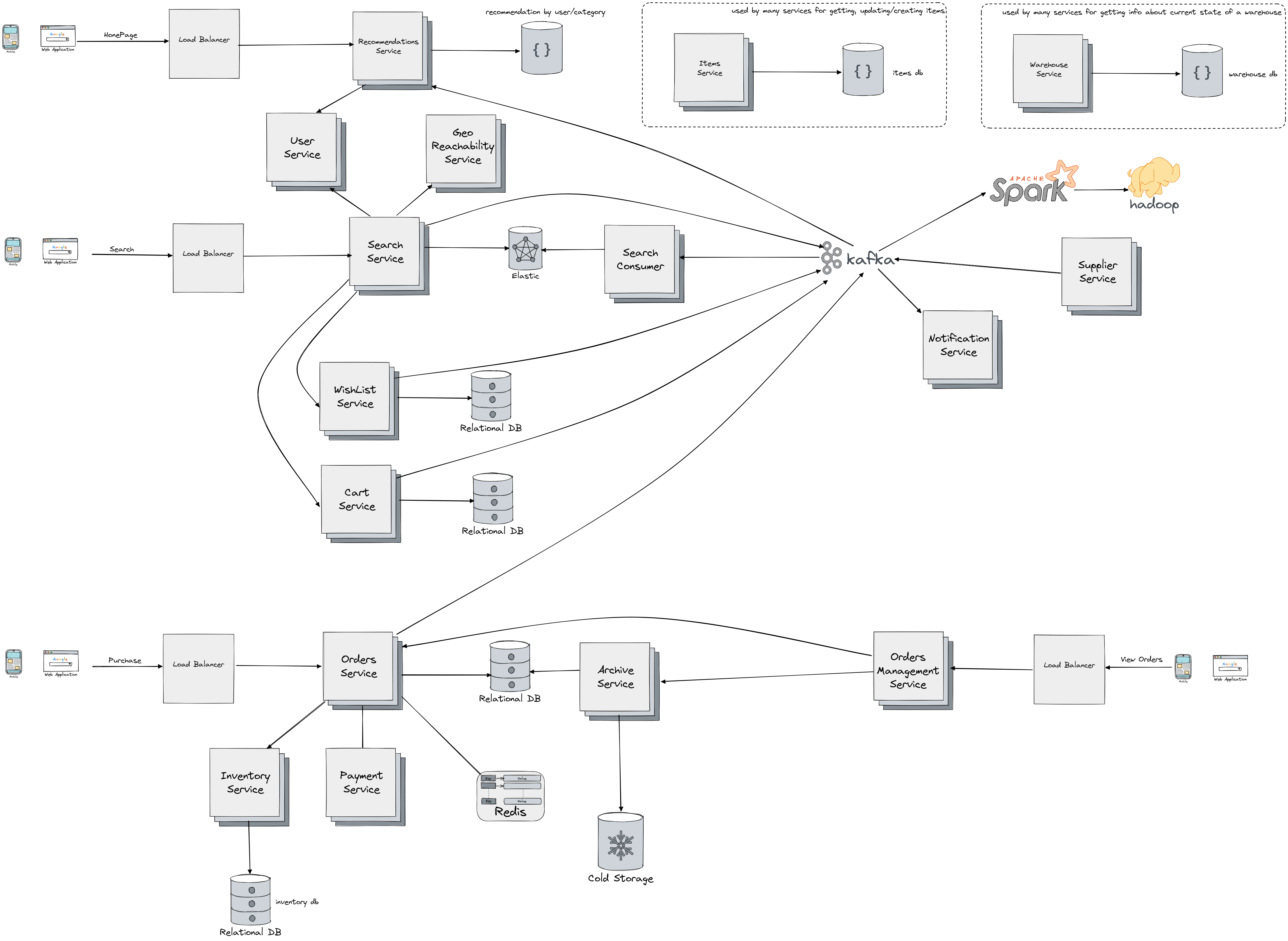
First let's discuss the HomePage flow:
- We use Load Balancer component to uniformly distribute the load coming from users and to redirect user request to the closest (or any other routing algorithm we might use) Recommendations Service
- Recommendations Service is an interface that sits on top of a NoSql database (column or document based) and gets/updates recommendations for certain user/category (or any other dimension/parameter). Recommendations are created as product of running Spark jobs/pipelines on collected events comming from WaitList Service, Order Service, Search Service and Order Service. Recommendations Service communicates with User Service which is component we use to get/update information about users.
Just like we have in Hotel Booking System Search Service is interface on top of Elastic enabling effective fuzzy search for the product and it's the foundamental component for the Search Flow. Search Service communication with Geo-Reachibility Service which calculates information about shortest path to the client from the warehouse (using information from the Warehouse Service) and if any valid path exists by using the information like geolocation we're getting from the User Service. Cart and WishList Services sit on top of seperated relational database clusters enabling us to scale them independently and they're source of events we use for our recommendation engine.
In the Purchase Flow we have the following components:
- Again we use Load Balancer to distribute the load towards the Orders Service
- Orders Service is responsible for orchestration of the purchase activity. It has connection to Inventory Service which track the current stock/quantities of the items (Note that each order could have multiple items, in any scenario where we need information about items we contact the Items Service), and also Payment Service used for processing invoices. Orders Service is also a component we used for communication (getting/updating) data from both Redis Cache and distributed relational database. Same like we have in Hotel Booking System we use relational database so we can support (distributed) transactions and ACID properties. Order Service sends events like order completed to Kafka so they can get propagated to interested event consumers. Why do need connection to Redis? Once all the rows are updated in relation database we're only waiting for the payment to processed, but we can't wait forever, so we have to store TTL (time to live) for each of the order in redis. If the payment goes through we can just evict the record from the Redis. But more interesting situation is when payment is successful but the event happens after the record has expired. In that case we can issue a transaction rollback (check Amazon Aurora for WAL log and transactions) and do a refund, or we can check to see if we have all items from the user order in inventory and do the transaction again.
- We use Archive Service to store the bookings information in a Cold Storage so we can free the space in releation database for active bookings, and so we can also perform analysis on the previous bookings via the Spark and Hadoop Cluster. If a user wants to View Orders we utilize Orders Management Service which sits as interface in front of active orders in relational database and archived cold storage for past orders.
There are two components we haven't covered yet. Notification Service is used to notify users on completion of actions like invoice, delivery data, order changes and similar. Supplier Service is used to communicate with Kafka that new items are available, so that information can be propagated to all interested event consumer like Search Service or WareHouse Service. All of the stateless service can be scaled horizontally so we can achieve the non-functional requirements, the actual problem is how to scale the databases/storage effectively. To learn more about distrubuted database built on top of Mysql check out the Amazon Aurora which goes in details how to design multi-regions, replicated and partioned databases. It's important to note that the booking operation should be atomic (that's why we choose relational database supporting ACID), and that we should support distribute transactions in order to update all required database rows, and payment processing. To get more infomation on how we can design consistent database with distributed transactions check out Google Spanner. To learn more about transactions and how to prevent common problems like phantom writes and read/write skews check out the Transactions. For calculating the top performing items we can utilize the Spark pipeline running on Hadoop, just like we did in Tiny URL.