Social Network
In the context of a social network platform like Facebook, the functional requirements are:
- Post: The ability to create and publish a text, image, or video content for other users to see.
- Like/Comment/Share: The ability for users to interact with posts by liking, commenting on, or sharing them with others.
- Add Friends: The ability for users to connect and follow the activities of other users on the platform.
- See Timeline/Newsfeed: The ability to view a consolidated and personalized view of all the posts made by friends and other users the user is following.
- See a User's Post/Profile: The ability to view a specific user's profile and all the posts they have made.
- Activity Log: The ability for users to view a record of their own activity on the platform, such as posts made, likes given, comments made, etc.
While for non functional requirements we have:
- Read heavy: The platform should prioritize fast and efficient reading of posts over writing new posts.
- Fast rendering and posting: The platform should be able to quickly render new posts and updates to the newsfeed and quickly process new post submissions.
- Lag tolerance: Important to note that lag is different than latency. For generating news feed for example we're expecting low latency (decrease request time), while lag references the delay of a single post for example being propagated to user news feed.
- Access pattern: The platform should be able to handle a large and unpredictable number of concurrent users accessing the platform from different regions and at different times.
- Global internet bandwidths and presence: The platform should be optimized for global internet connectivity and provide a fast and seamless experience for users from all regions.
- Scale: The platform should be able to handle 1.5 billion daily active users (DAU) and 2.5 billion monthly active users (MAU), with 95% of these users accessing the platform from mobile devices.
- Mobile optimization: The platform should be optimized for mobile devices, with a user-friendly interface and efficient use of limited mobile device resources.
- Content creation and processing: The platform should be able to handle the creation and processing of a large number of posts, with 200,000 images, 300,000 statuses, and 500,000 comments added every minute.
Segmenting users into categories can help a social media platform to optimize the user experience and improve engagement. The following are some categories of users that could be considered:
- Famous/Celebrity Users: These are users who have a large following and significant influence on the platform. The platform should provide these users with dedicated support and special features to help them engage with their followers.
- Active Users: These are users who have been active on the platform in the last 2-3 days. The platform should prioritize the content of these users and make it more visible in the newsfeed to keep them engaged.
- Live Users: These are users who are currently scrolling through their newsfeed and actively engaging with the platform. The platform should prioritize their content and provide them with a real-time, interactive experience.
- Passive Users: These are users who are not actively using the platform but still log in from time to time. The platform should provide them with relevant and personalized content on an on-demand basis.
- Inactive Users: These are users who have not been active on the platform for a certain period of time. The platform could offer them reminders or incentives to re-engage with the platform.
By segmenting users into categories and optimizing the user experience for each group, a social media platform can improve engagement, increase user satisfaction, and drive growth.
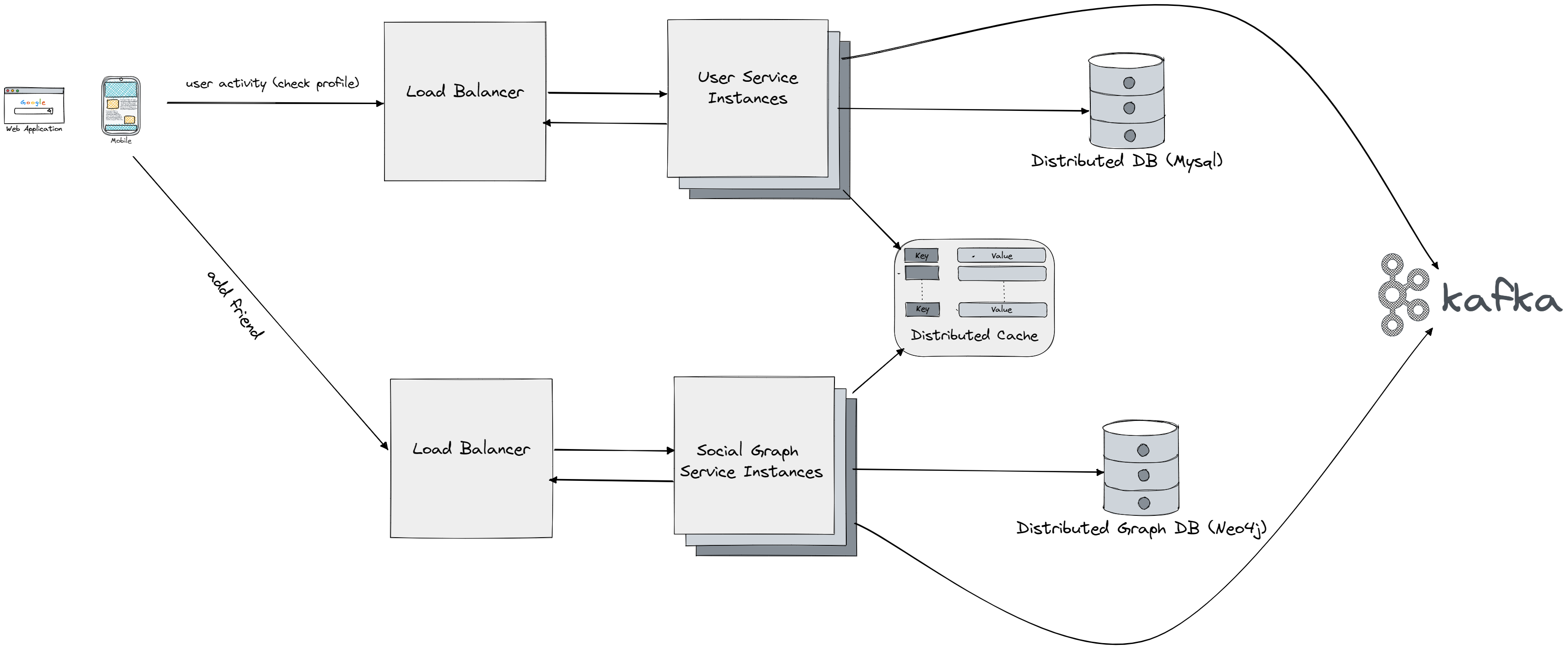
- User Service: This component is responsible for managing user accounts, including user registration, login, and profile management. It also handles user authentication and authorization.
- Login: The login process allows users to access their account and start using the platform. The user service component manages this process, which may include sending a verification email, requiring a password, or using multi-factor authentication.
- Checking Profile: This feature allows users to view their own profile and see information such as their posts, comments, likes, and followers. This information is stored in a database and may be cached in Redis for faster access.
- Redis Cache: Redis is an in-memory data structure store used as a cache to store frequently used information, such as user profiles, to reduce the load on the main database and improve performance.
- Kafka Stream Processing: Kafka is a distributed streaming platform that processes large amounts of data in real-time. It is used for fraud detection by collecting events and analyzing them for signs of suspicious activity.
- Social Graph Service: This component manages relationships between users, such as friendships, by storing user IDs and friend IDs in a graph structure in a database like MySQL or use a graph based database like Neo4j. This information is cached in Redis for faster access.
- Relevance: This feature allows users to see content that is relevant to their interests, such as movies, activities, etc. It is powered by analytics that analyze user behavior and suggest content that the user may be interested in.
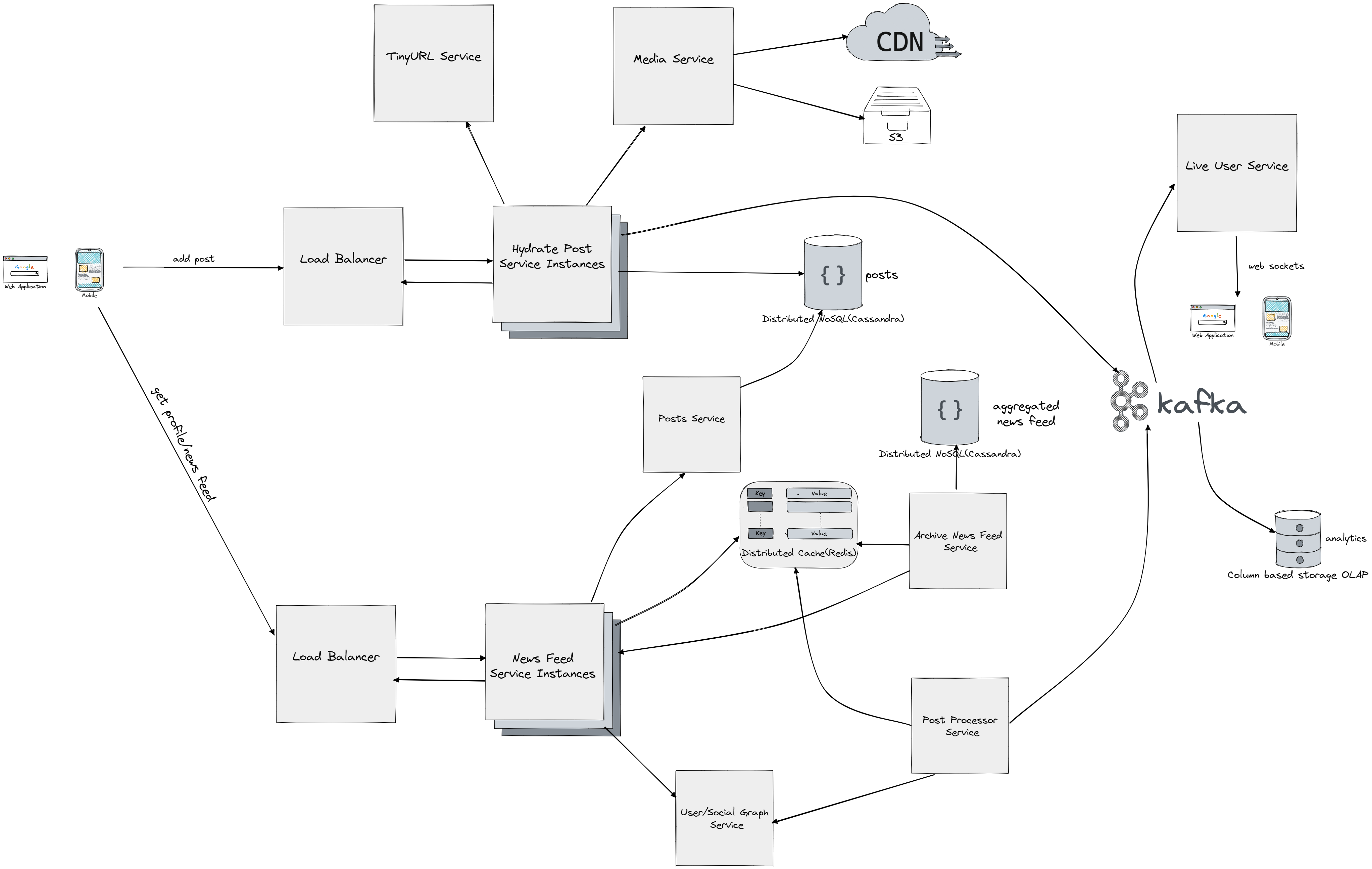
Several components work together to support the functionality of adding posts, generating newsfeeds, and providing a short URL service like we implemented before Tiny URL. The post processing component is responsible for adding relevance tags to posts and getting information about all friends of a user from Kafka. A classification model for posts is used for analytics, and lag is acceptable. For normal users, information is stored in Redis for quick access. For famous users, the data is only fetched on demand. This are the basics of fanout flow. Fanout is a process that allows posts to be distributed to all of a user's friends. There are two types of fanout models: fanout on write (push model) and fanout on read (pull model). Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages, which are discussed in order to determine the best approach for supporting the system. The fanout on write approach generates the news feed in real-time and sends it to friends immediately after a post is published. However, this can result in slow performance if a user has a lot of friends and is considered a hotkey problem. On the other hand, the fanout on read method generates the news feed during the time of reading and is more efficient for inactive users, but can be slow as the news feed is not pre-computed. A hybrid approach is adopted to reap the benefits of both methods and overcome their drawbacks. The push model is used for the majority of users for faster news feed retrieval, while the pull model is employed for celebrities or users with a large number of friends to avoid system overload. The cache invalidation occurs after a set interval. After a post is made, the system places an event in Kafka to indicate that the user is live, which is then propagated to the live user service. The live user service has open websocket connections with all live users. The media service is responsible for handling video and images, which are stored on a content delivery network (CDN) such as Amazon S3. However, if the popularity or hit rate of an image decreases, it may be removed from the CDN. Cassandra is used to handle high loads of both reads and writes, and is able to handle the large amounts of data being generated. The Archival News Feed component serves as a materialized view or snapshot in time for the user's news feed. When a user requests their news feed, the system first checks Redis for any recent data. If there is no recent data available in Redis, the News Feed Service is called to generate a new news feed for the user. The Archival News Feed component then stores the generated news feed in Cassandra. However, only the IDs of the posts, not the actual data, are stored. This allows for efficient storage and retrieval of data, as the real data is only populated when a user requests it. The use of Redis and Cassandra in this manner allows for a balance between speed and scalability, as Redis provides quick access to recent data, while Cassandra can store large amounts of data for longer-term retrieval. The Archival News Feed component serves as a backup to Redis and ensures that a user's news feed can be reconstructed even if the Redis cache is lost or outdated.
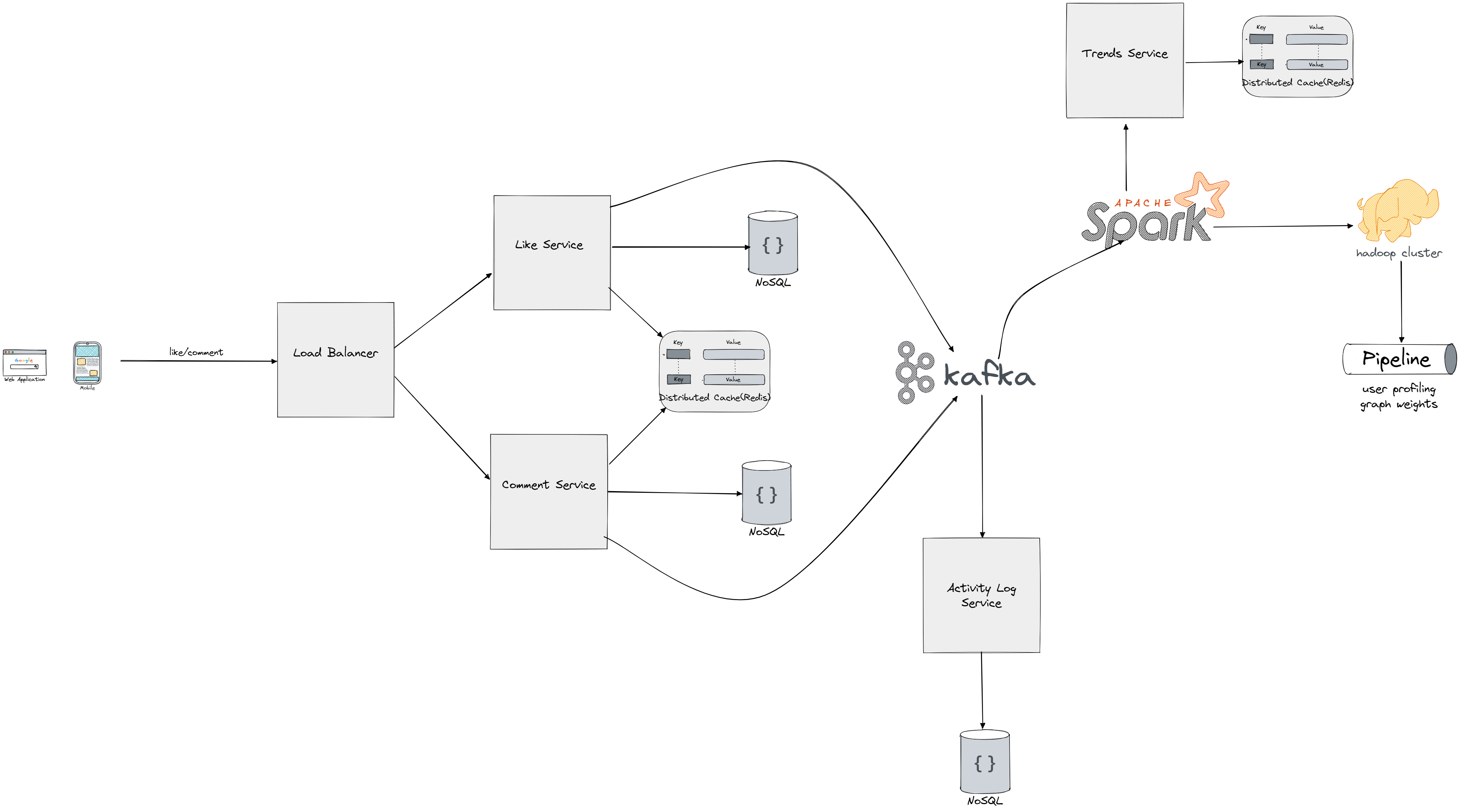
The "like/comment UI" and related components are part of the user interface and user experience of a social media platform:
- Like/Comment UI: This is the interface that users interact with to like or comment on a post. It may include buttons, forms, or other types of input controls that allow users to express their reactions to content on the platform.
- Redis Count of Likes/Comments: Redis is used to store the count of likes and comments for recent posts, allowing for fast retrieval and display of this information in the UI.
- Shared Posts: When a user shares a post, it creates a new post that references the original post as its parent. This allows for a chain of posts to be created, with the original post at the root and subsequent shares branching off from it.
- Stream Processing Pipeline: The stream processing pipeline is a series of processing steps that take raw data, such as user interactions with posts, and transform it into meaningful information. This information can be used for a variety of purposes, such as calculating post popularity, detecting fraud, and generating user profiles. We're utilizing hadoop cluster in same fashion we do in MapReduce servers, processing large amounts of data in a distributed manner.
- User Profiling Jobs: User profiling jobs use the processed data to generate user profiles, which include information about the user's interests, behavior, and other relevant data. The tags associated with user profiles are managed by the user service component.
- Graph Weight Jobs: Graph weight jobs calculate the importance of relationships between users, allowing the platform to make recommendations based on which users are most relevant to each other. The weight of a relationship may be influenced by factors such as frequency of interaction, shared interests, and more.
- Trends: The platform may also track trends by analyzing the content that is being shared and the words and phrases that are being used frequently. This information can be used to identify popular topics and generate recommendations for users based on what is currently popular.
Monitoring
Tracking resource utilization and creating alerts is important for several reasons:
- Performance monitoring: Resource utilization provides valuable insight into the performance of a social media platform and its infrastructure. By tracking resource utilization, administrators can identify areas of the platform that may be struggling under heavy loads and take steps to improve performance.
- Capacity planning: Resource utilization data can be used to plan for future capacity needs and ensure that the platform has enough resources to meet the demands of a growing user base.
- Cost optimization: By keeping track of resource utilization, administrators can optimize the use of expensive resources such as computing power, storage, and network bandwidth, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Early detection of issues: By creating alerts, administrators can be notified of potential issues with the platform in real-time, allowing them to quickly respond and resolve problems before they become critical.
- Improved reliability: Monitoring resource utilization and creating alerts helps ensure that the platform is reliable and provides a stable user experience. This is critical for maintaining user trust and satisfaction.
Finally it's important to note that we will have horizontal scalling for each other services, in other words additional instances can be added when the load on our system increases.