Design Uber
Uber is a multinational transportation network company that offers a variety of services, including ride-hailing, ride-sharing, and food delivery. The company was founded in 2009 and has since become one of the largest and most well-known companies in the sharing economy. Uber operates in over 700 cities worldwide and allows users to quickly and easily book a ride through its mobile app. The app also provides real-time updates on the status of the ride and allows users to rate and review their experience, helping to maintain high levels of service quality. Let's first go over our functional requirements:
- Real-time Cab Visibility: This functionality provides users with the ability to dynamically view and assess the availability of cabs in close proximity to their current location. This feature integrates cutting-edge mapping technology to showcase the cab type, driver information, and an accurate estimate of the distance between the user's location and the available cabs.
- Predictive ETA and Cost Calculation: This feature offers users a comprehensive understanding of the expected time of arrival (ETA) and the approximate cost of their cab ride. The system calculates the ETA based on real-time traffic conditions and the distance to the destination, providing users with a reliable estimate of the duration of the ride.
- Convenient Cab Booking: This functionality allows users to book a cab with just a few taps on their mobile device. The system integrates a seamless booking process that requires minimal user input, providing users with a hassle-free experience.
- Location Tracking: This feature provides users with the ability to track the location of their cab in real-time, from the time of booking until the completion of the ride. This ensures the highest level of safety and security for both riders and drivers.
For the non-functional requirements we have the following:
- Global: The system must have a globally distributed network of servers to reduce latency and provide a fast and responsive experience to users all over the world.
- High Consistency: The system must be designed to be highly consistent, meaning that the results of an operation should be the same every time it is executed. This will help to ensure that users receive the same level of service quality, regardless of when or where they use the system.
- High Availability: The system must be designed to be highly available, meaning that it must be operational and accessible to users at all times. This will ensure that users can book a cab whenever they need one, without interruption.
- Low Latency: The system must have a low response time to provide an immediate and smooth experience to users. This will help to ensure that users can quickly book a cab and track its location in real-time.
- Scalability: The system must be able to scale to meet the demands of 100 million monthly users and 15 million rides per day. This will ensure that the system can handle a large number of users and ride requests, and that it can continue to operate effectively as usage increases.
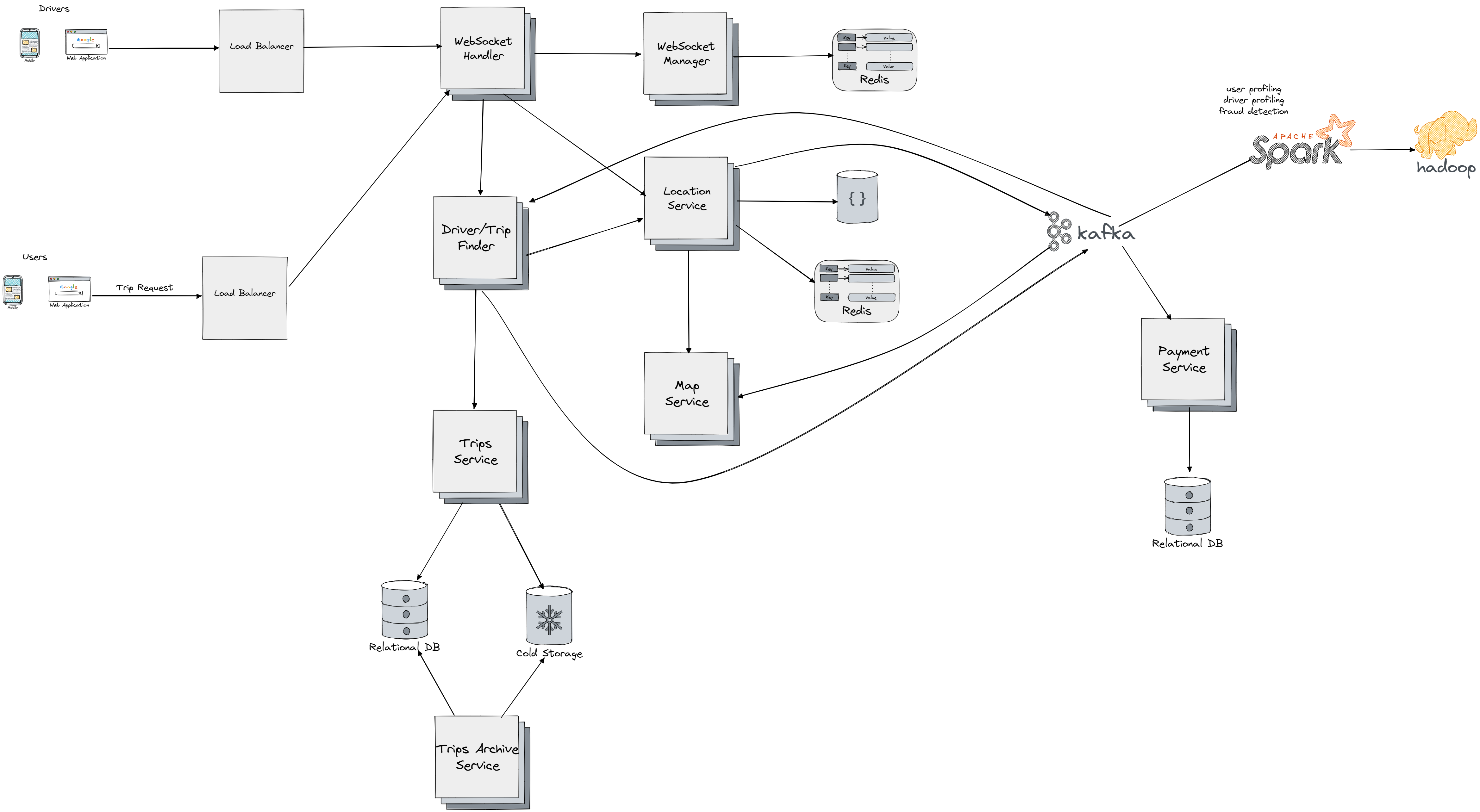
Let's go over each component and describe the flow in details:
- Load Balancers - to uniformly distribute our load to WebSocket Handler and other services.
- WebSocket Handlers - It keeps a bi-directional connection with a certain user, it sends an events each time there is a new message for the user it maps to, leading to message appearing on user device. This component will allows to send any notification/event to the user or the driver during the trip.
- WebSocket Manager - This component manages the mapping of users to WebSockets. It sits in front of distributed cache (Redis) which store the mapping between users and websocket handlers.
- Location Service sends events to Kafka about current location of the driver and the client. It communication with a Map Service which we implemented in Google Maps and handles all the responsibility of segmentation (explained below), finding the best route, calculating distance and cost, determining what segment the users and drivers are currently located. Location Service stores the infomation about the current location (segment) in database and also caches it in cache (for example Redis) to speed up the retrieval. It also sends events to Kafka about (change of) location which will be than later processed by Spark and Hadoop clusters and propagated back to Location Service and Map Service (new routes, sparse segments, hot segments and similar). Stream processing and ML algorithms running as Spark jobs are also use to classify users and drivers based on their recent trips/behaviour.
- Driver/Trip Finder user Location Service find best driver options per user request , stores the trip by communicating with Trip Service which main responsibility is to do operations on trips and storing/getting the info from active trips stored in relational database, and archived trips stored in cold storage nosql database. Driver/Trip Finder also sends an event to Kafka when the trip has ended, so that event can be later consumed by Payment Service which processes payment invoices and stores the data in relational database (transactional based following ACID). All events are propagated back through WebSocket Handlers to users and drivers.
- Trips Archive Service gets the data from the current active trips stored in relational database and if they're not required anymore to be in active state (payment processed), it stores them in cold storage to free up the space in the relation database.
Let's dig deeper into segmentation. In the context of a ride-hailing service, segmentation refers to the process of dividing a geographical area into smaller segments or "zones" in order to manage the deployment of drivers more effectively. The goal of segmentation is to ensure that there are enough drivers in a particular zone to meet demand, while also avoiding over-saturation that could lead to decreased earnings for drivers. To divide a segment if there are too many drivers, the geographical area can be divided into smaller segments, and the number of drivers in each segment can be reduced. This will help to distribute the available drivers more evenly, ensuring that there is a good balance between supply and demand in each segment.On the other hand, if segments are sparse, meaning that there are not enough drivers in a particular area to meet demand, then those segments can be combined to create a larger segment with a higher concentration of drivers. This will help to ensure that there are enough drivers available in the combined segment to meet demand. The goal of segmentation is to optimize the deployment of drivers in a way that ensures a high level of service quality for users while also maximizing earnings for drivers. The process of segmentation may need to be updated regularly to reflect changes in demand patterns, and to ensure that the deployment of drivers remains optimized over time.